What a Medical Database is and How We Can Use it
With the advancement of information technology in the medical industry, all sorts of medical data are now digitally managed.
Big data, known as medical databases, are being utilized to gain profound medical knowledge. A medical database is an integrated database that compiles all the medical treatment information provided by medical institutions.
In this column, we will explain the role of medical databases and how they can be used.
What is a Medical Database?
What exactly is a medical database in the first place? To begin with, let’s take a look at the outline and characteristics of a medical database.
What is a Medical Database?
A medical database is an integrated database in which medical information collected from medical institutions and patients are stored. Medical information here refer to information such as prescribed drugs to treat patients’ injuries/illnesses, clinical laboratory test results, and so on.
The types of data handled in medical databases include the following:
- Expenses invoice data
Collected from medical institutions, pharmacies, health insurance associations, etc. - Medical institution data (HIS*/DPC/EMR data) (*HIS = Hospital information system)
Electronic medical records (EMR), orderings, diagnostic imaging, lab data results, etc. - Prescription data
Patient’s prescription history data, patient guidance texts, etc. - Voluntary adverse event report data
The above data collected from each medical institution into the medical database will be used for secondary purpose and for research to provide more advanced and safer medical care.
Characteristics and Purposes of Medical Databases
One of the key characteristics of medical databases is that they enable experts to utilize vast and diverse safety information efficiently and effectively. In particular, the data collected into medical databases are often used for rapid evaluation of risks and benefits of drugs.
In the current medical system, the reporting method of drug side effects has its limitations for safety measures, and the need to consider better measures is under discussion.
- Unable to keep track of how many people took the medication
- Difficult to differentiate between primary disease conditions and side effects
- Unable to compare the frequency of side effects with other drugs
- Unable to compare the frequency of side effects before and after the safety measures is enforced
- Unless the medical institution reports it, the side effects are not known in the first place
As previously mentioned, it is difficult to grasp the side effects and harmful effects of medicines if the evaluation uses only a small amount of data. Therefore, it is important to build a large-scale medical information database to correctly evaluate the incidence rate of side effects and the effectiveness of safety measures.
In the U.S. and European countries, huge databases of tens of millions of people are already in operation, and they are being used to evaluate the safety of drugs. In order to conduct the same level of safety evaluation in Japan as in other countries, it is said that data of several to ten million people are needed [*1], and a project to develop the infrastructure for a national medical database is currently underway.
[*1] 厚生労働省:医療情報データベース基盤整備事業について[pdf]
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi/2r9852000002za66-att/2r9852000002zdgp_1.pdf
Types of Medical Databases
It is characteristic that medical databases are not operated and provided by a single institution, but by various institutions. There are a wide variety of medical databases in Japan and abroad, but we will introduce some of the typical ones here.
- NDB (National Database)
A medical database for public interest purposes provided by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). - MID-NET
A medical database that collects electronic medical records and other data from 23 major hospitals nationwide, used for post-marketing surveillance or research with high public interest - JADER
Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) Database - Other medical databases
Medical databases operated by private for-profit companies and educational research institutions
There are strict conditions and big hurdle for using medical databases operated by public institutions such as NDB and MID-NET. Therefore, medical institutions and pharmaceutical companies normally conduct research while also using medical databases provided by private companies.
How a Medical Database is Created
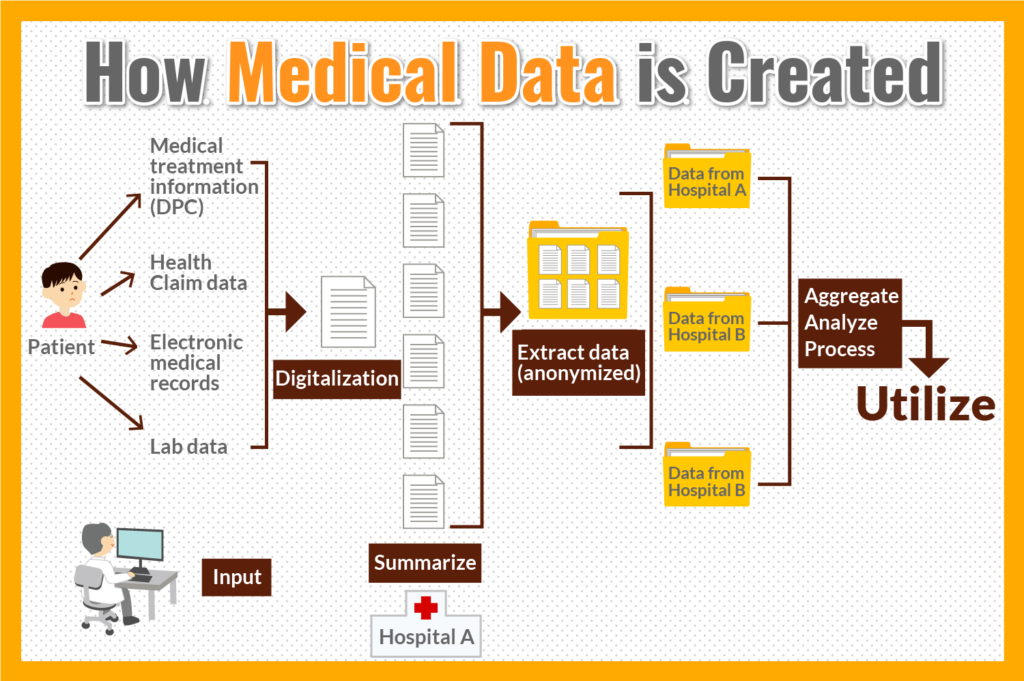
What is the actual process of providing information to a medical database and using the collected information? The process of creating a medical database is as follows:
- Medical institution enters electronic medical records and orderings
- Standardized storage system converts the information into data
- Summarizes data into an integrated data source
- Extracts data other than personal information by extraction system
- Aggregates the extracted individual forms in a multi-facility integrated processing system
- Analyzes with analysis system
- Aggregates, processes, and utilizes as necessary
Users of a medical database can only handle the data after extraction, which is performed in the fourth step. This data is characterized by the fact that it does not contain entire information including names, addresses, and dates of birth, and only anonymized processed information that protects privacy is extracted.
Types of Medical Data
Medical data sounds simple enough, but it can actually be categorized into three types. Let’s take a closer look at the different types of medical data to further understand medical databases.
DPC Data
DPC data refer to information collected and managed by the MHLW in accordance with the provisions of Section 5, Item 3 of the “Method of Calculating the Amount of Expenses Required for Medical Treatment in Hospital Wards, Designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare.”
Simply put, it refers to the nationally standardized data of medical treatment information which is consisted of the following six designated files. [*2]
- Format 1 file: Simplified medical record information
A simplified version of the discharge summary. It contains the patient’s date of birth, dates of admission and discharge, the name of the disease, and details of treatment, and is a document that provides a general overview of the patient. - Format 3 file: Facility information
This is a document that summarizes information on basic inpatient fees, etc. that have been reported. - Format 4 file: Information on medical treatment other than insured medical treatment
This document summarizes the implementation of medical treatment other than insured medical treatment, such as advanced medical treatment and public expenditure. - EF integrated File: Fee-For-Service points information based on the medical service fee points
This is a document that summarizes how many reimbursable medical treatments have been performed on a fee-for-service basis. It contains data identification numbers, dates of admission and discharge, and medical treatment categories.
*1 point is equivalent to 10 Japanese Yen. - D File: Comprehensive health claim information
This is a document that compiles information on patients’ medical fee claims, calculated by using the “Diagnosis Procedure Combination (DPC) Points Table” established by the MHLW, which consists of the disease names and details of medical treatments. - Outpatient EF integrated file
This is a document that compiles fee-for-service point information based on the medical service fee table for outpatients and fee-for-service claim information for outpatients.
The collected data are utilized by administrative agencies, municipals, and public corporations.
Hospitals that have adopted the DPC system are called “DPC eligible hospitals.” To be eligible, hospitals must undergo a review by the MHLW and submit necessary documents.
[*2] 厚生労働省 DPCデータ提供事業者:DPCデータの提供について [pdf]
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/06-Seisakujouhou-12400000-Hokenkyoku/0000188034.pdf
Health Claim Data
Health claim data is a common name for medical fee statements. It contains the injuries/illnesses names of the patients who visited the medical institutions, details of the performed medical procedures, and the associated billing information.
Data are generated not only for hospitals but also for dental clinics and pharmacies, and are compiled for each patient once a month. Currently, more than 90% of health claims are digitalized [*3] and it makes it easier to use the data than ever before.
[*3] 実験医学online: Receipt data
Electronic Medical Records and Lab Data
Electronic medical records and various laboratory data are also important data that make up a medical database. Information on injuries and illnesses, prescriptions, injections, laboratory test results, and dietary information are also collected and integrated into the database. These are essential information for the utilization of medical databases because they provide a more detailed overview of symptoms and treatments.
Examples of Medical Big Data Utilization
Let’s look at some utilization examples of medical big data, including medical databases at the end.
Utilization in Medical Field
The first possible example is the use of medical databases in the medical field. In fact, according to the “Utilization of Medical Big Data in Japan” compiled by the Japan Medical Association, it is suggested that medical databases are effective in predicting and early detection of diseases. [*4]
When a patient is examined at a medical institution, an analyzed document will be created based on the information from the medical interview, examination, and prescription drug names. By aggregating the data of patients with the same symptoms from the medical database, the data can be used to identify the name of the disease and determine the progress of the disease.
Even if the patient has symptoms that he or she is not aware of, the examined image data can be used to search for other patients with similar conditions and address slight abnormalities that might otherwise be overlooked. The medical database can be used in the medical field to promote a healthier life for patients and help improve their QOL.
[*4] 日本医師会:日本の医療ビッグデータの利活用
https://www.kantei.go.jp/jp/singi/kenkouiryou/jisedai_kiban/dai5/siryou7.pdf?_fsi=ubTniEkS
Development of New Drugs
Medical databases can also be used for the development of new drugs.
When developing a new drug, there are many hurdles to overcome, such as the enormous cost and time-consuming development process, and the collection of clinical trial data using the new drug. Medical databases can be utilized for epidemiological studies by these pharmaceutical companies and forecasting of their own products.
They can help to identify potential new drug targets and collect cases in the development area more efficiently and at a lower cost. The information in medical databases are also useful in assessing the risk of side effects and harmful effects of drugs and improving safety.
Medical Databases will Support the Future of the Medical and Pharmaceutical Fields!
A medical database is an integrated database in which medical information collected from medical institutions and patients are stored. By collecting and analyzing information such as expenses invoice data, medical institution data, and pharmacy data, this big data can be of great help to medical practices at medical institutions and new drug developments at pharmaceutical companies.
Medical databases are provided not only by public institutions but also by private companies. Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. collects medical and health information through its data network service. Please feel free to contact us if you are interested in using medical database.
For More Information, Please Contact Us Here
About Japanese Healthcare System

What you need to know about the healthcare system in Japan before using the data.
SERVICE

In addition to various web tools that allow you to easily conduct surveys via a browser using our medical database, we offer data provision services categorized into four types to meet your needs and challenges: "Analysis reports" "Datasets," "All Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service," and "Specific Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service.

© Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.