What is Clinical Research? Its Definition and Research Process
Clinical research is being conducted every day around the world for the advancement of medicine. In particular, clinical trials, which are one major type of clinical studies, are an essential process for the creation of new drugs.
This column will explain the definition of medical research, how it is done, and the process of creating new drugs.
Contents
- Clinical research refers to medical research on human subjects
- The relationship between clinical research, clinical study, and clinical trial
- The process of developing a new drug
- What is the relationship between clinical research and EBM?
- Clinical research such as clinical trials and clinical studies are essential for the development of medicine
Clinical research refers to medical research on human subjects

Clinical research refers to medical research on human subjects.
Medical technology is improving day by day, and more and more diseases that could not be cured some time ago are now being conquered. This is due to the fact that people involved in the medical field continue to conduct clinical research in various forms.
Some medical fields are studied over a long period of time, sometime extending over many years or decades.
The purposes of clinical research are to elucidate the causes of diseases, establish treatment methods, prevent diseases, and so on. According to the “Ethical Guidelines for Clinical Research” defined by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the subjects of clinical research are mainly classified into the following four categories.
- Investigation of the cause of injury/ illness
- Understanding of clinical conditions
- Improving or validating the effectiveness of methods for preventing injury/ illness.
- Improving or validating diagnostic or treatment methods in medicine.
According to the guidelines of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the purpose of clinical research is to identify factors that affect health and to accumulate useful knowledge. Improving medical technology through clinical research will also lead to improved quality of life and health for patients.
The relationship between clinical research, clinical study, and clinical trial
Clinical research is a general term for medical research conducted on human subjects. Clinical research includes not only clinical studies, but also various other types of research such as epidemiological studies, validity studies, and prognostic factor studies.
Clinical studies in clinical research are studies to determine the efficacy and safety of a drug or treatment. Clinical studies are designed to follow a methodic planning process where the concepts elaborated in laboratory and in animal testing will be challenged in the human metabolism, so as to ensure that the drug has an effect on the disease to treat, that it does it with an acceptable, predictable and manageable level of toxicity, and finally achieves the treatment goals in a more efficient manner than existing therapies.
A clinical trial is a trial to examine the mechanism, effectiveness and safety of a drug
A clinical trial is also the process of carefully examining the safety of a drug to provide all necessary guidance to healthcare professionals who will use the drug.
Newly developed drugs are not immediately used in hospitals and pharmacies. After the drug is conceptually designed, it is first tested on animals to test its effects and side effects. After confirming the safety of the drug, clinical trials are conducted to test the effects of the drug on humans.
Clinical trials are divided into phases or steps, from Phase I through Phase III trials prior to submitting the data to health authorities to obtain the market license. It generally takes five years or more for a new drug to pass through all the trials. Let’s take a closer look at each stage of clinical trial development until the New Drug Application (NDA) is submitted to health authorities.
Phase I clinical trial
In Phase I of a clinical trial, a new drug is administered in various doses to healthy adults and monitored to determine the relationship between dose and effect, including side-effects, also known as adverse drug reactions (ADR)
The purpose of Phase I clinical trial is to investigate whether the effects that were confirmed in the animal experiment phase will also appear in the human body and whether side effects will occur and at which dose. In Phase I, in addition to the efficacy, how the drug is absorbed, transformed (also known as metabolized) and finally excreted from the body is carefully examined.
Phase II clinical trial
Phase II of clinical trial development is divided into two phases, but this time the drug is administered to patients rather than healthy volunteers. The purpose of the first phase (also known as Phase IIa) is to test the efficacy and safety of the drug with the help of dozens of patients who are eligible for the drug.
If no major problems occur in the first phase, more patients will be asked to check the balance of dosage and administration as well as the safety and effectiveness of the drug in the Phase IIb part.
Phase III clinical trial
In Phase III of a clinical trial, a larger number of patients with the target medical condition are asked to cooperate in order to investigate the effectiveness of the drug in comparison with established therapeutic approaches. This phase is characterized by checking the effectiveness and safety of the drug, as well as comparing it to drugs that have been approved for the treatment of the targeted diseases.
Rules for conducting clinical trials
In a clinical trial, all the effects of a drug are not known so it requires various simulations and assumptions to be administered for investigation. For this reason, there are strict rules for clinical trials, and they are investigated and reviewed as appropriate.
There are national rules for conducting clinical trials
The government has established rules called “Standards for the Conduct of Clinical Trials of Drugs” regarding clinical trials. The most important part of these standards is to protect the safety of people who cooperate in clinical trials and to guarantee their human rights.
Continuation of the clinical trial requires review by the institutional review board
When conducting a clinical trial, it is necessary to go through a review by the local institutional review board (IRB) in the medical institutions where the trial takes place. If the content of the clinical trial is not approved, the trial cannot be performed.
In addition to hospital staff such as doctors, nurses, and pharmacists, IRB also has external members such as university staff and welfare related staff. The involvement of people from various positions ensures the fairness of the review process.
The cooperation of clinical research coordinators is also essential
Clinical trials are usually conducted by hospital personnel plus a clinical trial coordinator.
Clinical trial coordinators are responsible for coordinating the smooth implementation of clinical trials by providing care and support to patients who are eligible for the trials.
The process of developing a new drug
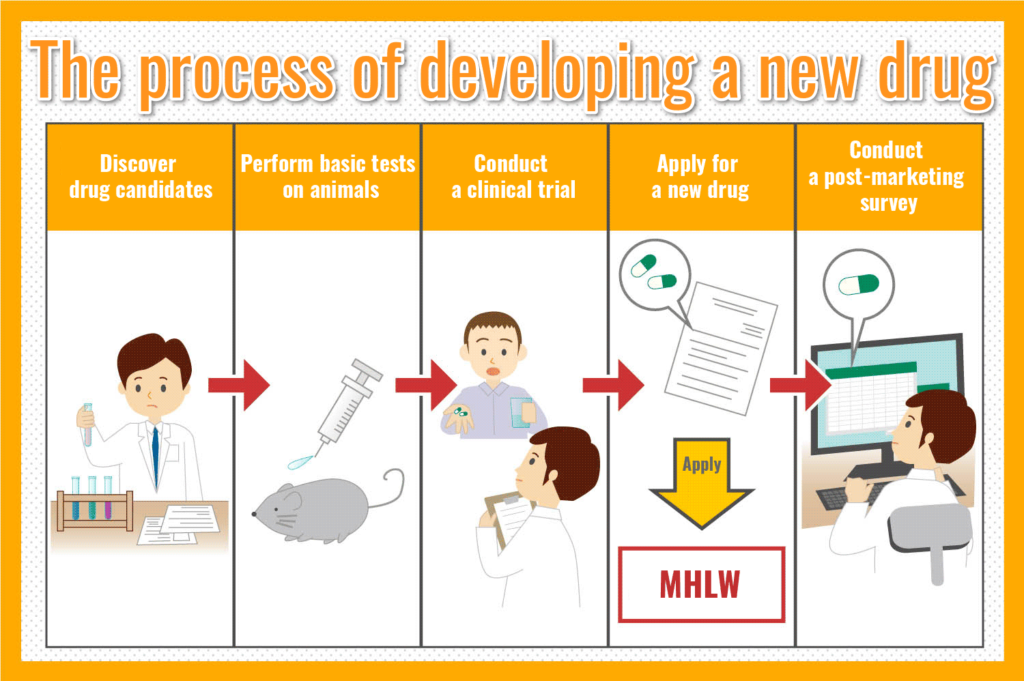
All over the world today, many researchers and doctors are working on the development of new drugs. Here is a brief explanation of the process of creating a new drug.
Discover drug candidates
In the field of new drug research, many people are working to find substances that are effective to treat diseases. During their research, candidates for drugs that have new effects that have never been seen before are sometimes discovered, providing hope for a better, more efficient and possibly safer cure.
Perform basic tests on animals
Once a drug candidate is found, it is first administered to animals such as rats, dogs, and monkeys. At this stage, the effectiveness of the drug is examined in detail, as well as the possibility of serious side effects.
Conduct a clinical trial
New drug candidates that have not caused any problems in animal experiments are administered to humans in clinical trials. The purpose of a clinical trial is to investigate whether the drug is effective in the human body and whether it causes any side effects.
New Drug Application Submission
Once sufficient clinical trial data have been gathered and analyzed, a new drug application is filed with the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Once the application is filed and the drug is approved, it can be used at hospitals and pharmacies.
Conduct a post-marketing survey
The effectiveness and side effects of the drug will continue to be tracked and improved into a better drug.
What is the relationship between clinical research and EBM?
In the field of clinical research, the concept of EBM (Evidence-based Medicine) was proposed in 1990.
In the past, some medical professionals provided medical care based on their subjective and common sense. As a result, there were many cases of disparities in medical care among hospitals even in the same country governed by common regulatory rules.
EBM is medicine based on the latest reliable data. The field of medicine has evolved dramatically through ongoing clinical research around the world and is now able to provide solid evidence to improve treatment outcomes.
The results of clinical research, which is practiced all over the world, must be efficiently linked to the practice of medicine. For this reason, it is crucial to evaluate the results of clinical research using the criteria of EBM.
In EBM, researchers and doctors need to refer to systematic reviews of scholarly articles for evidence, rather than making subjective judgments. A systematic review is a comprehensive study of a subject, summarizing the results, and analyzing and integrating the results.
Emphasizing EBM leads to the provision of solid medical care based on medical evidence.
Clinical research such as clinical trials and clinical studies are essential for the development of medicine
In the field of clinical research, various studies such as determining the causes and pathophysiology of diseases and exploring treatment and prevention methods are being conducted. Among these, clinical trials, which are used to create new drugs and demonstrate their effectiveness, are an indispensable step in helping people overcome illness.
As a result of relentless clinical research by researchers and doctors, cures and prevention methods for many diseases are being established today.
MDV operates medical information systems and provides consulting services to medical institutions. Please refer to the MDV website for more detailed materials on clinical research and medical data.
For More Information, Please Contact Us Here
About Japanese Healthcare System

What you need to know about the healthcare system in Japan before using the data.
SERVICE

In addition to various web tools that allow you to easily conduct surveys via a browser using our medical database, we offer data provision services categorized into four types to meet your needs and challenges: "Analysis reports" "Datasets," "All Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service," and "Specific Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service.

© Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.