An Introduction to Health Economics and Outcomes Research (HEOR): Concepts, Approaches, and Objectives
Growing Awareness of HEOR in Japan
In recent years, awareness of HEOR has increased in Japan. While HEOR is well-established as a discipline in the United States, its recognition in Japan remains relatively low. This article explores the key concepts, methodologies, and objectives of HEOR, along with an overview of health technology assessment (HTA) and Japan’s cost-effectiveness evaluation system.
Understanding Health Economics and Outcomes Research (HEOR)
HEOR involves the statistical analysis of the economic impact of treatments and their effects on both patients and society. It plays a central role in health technology assessment (HTA), which evaluates the value of medical technologies in improving health outcomes. The primary goal of HEOR is to optimize the delivery of evidence-based therapies to patients in a cost-effective manner.
What is Health Technology Assessment (HTA)?
HEOR serves as a key indicator in HTA, which examines medical, social, economic, and ethical aspects of healthcare technologies, including pharmaceuticals and medical devices. HTA findings support healthcare decision-making by assessing the costs and benefits of medical innovations.
With continuous advancements in medical technologies, new treatment options, drugs, and medical devices have significantly improved patient longevity and quality of life. However, these innovations require substantial financial investment, placing pressure on healthcare systems. HTA helps evaluate the cost-effectiveness of medical technologies, guiding decisions on appropriate treatments and resource allocation.
Japan’s Cost-Effectiveness Evaluation System
Japan introduced a cost-effectiveness evaluation system in April 2019 as part of its HTA framework. The system ensures that pharmaceutical and medical device prices align with their cost-effectiveness, assessing whether a product’s benefits justify its costs. If a drug or medical device is found to have low cost-effectiveness, its price may be reduced.
As medical technology advances, some new treatments come with exceptionally high costs. Given Japan’s universal healthcare insurance system, there are concerns about the financial sustainability of these expensive treatments. The cost-effectiveness evaluation system aims to alleviate this burden by ensuring that pricing reflects actual value
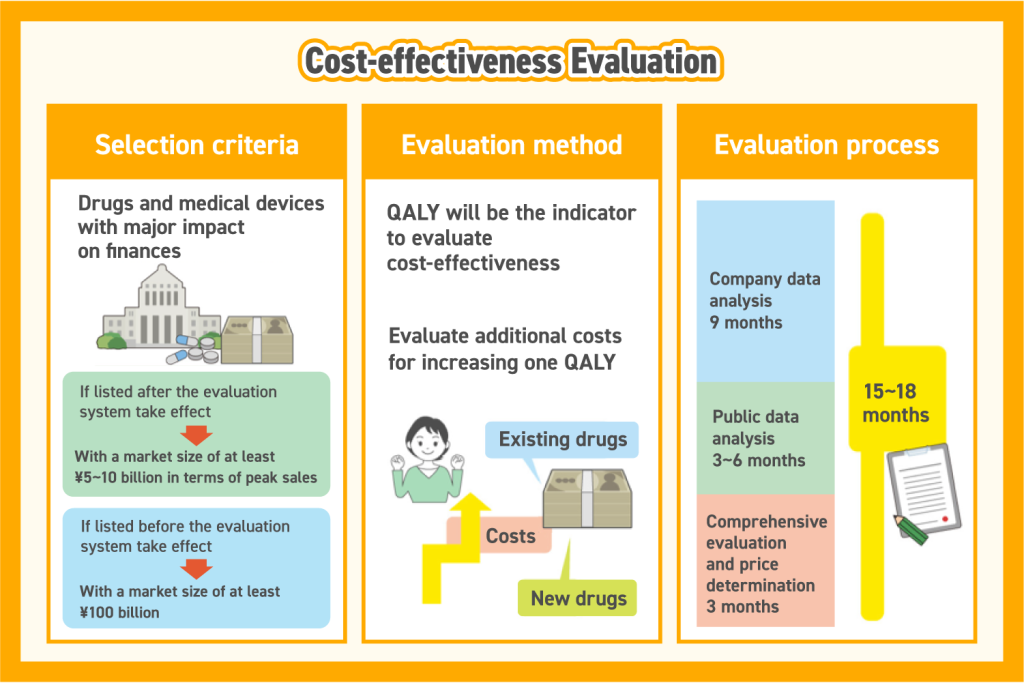
Selection Criteria for Evaluation
Not all drugs and medical devices are subject to cost-effectiveness evaluation. The system primarily targets products with a significant financial impact, determined by market size.
- Newly listed products (post-implementation of the system) must have an estimated market size of at least ¥5–10 billion in peak sales, depending on the category.
- Existing listed products (pre-implementation) must have a market size of at least ¥100 billion.
Additionally, prevention of excessive medication and unnecessary hospitalization are also considered as one of the benefits to the patients.
Evaluation Method
The cost-effectiveness evaluation system uses Quality-Adjusted Life Years (QALY) as a key metric. QALY measures both quality of life (QOL) and survival years by multiplying QOL—rated on a scale from 1 (perfect health) to 0 (death)—by the number of years lived. A higher QALY value indicates greater cost-effectiveness.
Evaluation Process
Once a product is selected for evaluation:
- The manufacturer conducts an initial analysis.
- The National Institute of Health Sciences (NIHS) performs a public review and reanalysis.
- A specialized organization conducts a comprehensive evaluation.
- Based on the findings, Chuikyo (Central Social Insurance Medical Council) determines pricing adjustments.
The entire evaluation process typically takes 15–18 months:
- Manufacturer analysis: 9 months
- Public review: 3–6 months
- Comprehensive evaluation and pricing decision: 3 months
Strengthening Awareness and Implementation
Japan’s healthcare system faces financial challenges due to a declining birthrate and an aging population. Given these constraints, HEOR, HTA, and cost-effectiveness evaluation systems play a crucial role in ensuring efficient healthcare resource allocation.
These systems depend on the collection and analysis of medical data, requiring efficient processing of diverse information sources. Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. (MDV) provides data network services and advanced analytical tools, offering in-depth insights into healthcare trends. As one of Japan’s largest real-world data (RWD) vendors, MDV supports the implementation of HEOR, medical technology assessments, and cost-effectiveness evaluations, contributing to the sustainable development of Japan’s healthcare system.
For More Information, Please Contact Us Here
About Japanese Healthcare System

What you need to know about the healthcare system in Japan before using the data.
SERVICE

In addition to various web tools that allow you to easily conduct surveys via a browser using our medical database, we offer data provision services categorized into four types to meet your needs and challenges: "Analysis reports" "Datasets," "All Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service," and "Specific Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service.

© Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.