What Are Intractable Diseases?
The term “intractable disease” may suggest a condition that is difficult to treat, but in Japan, it is defined based on specific criteria beyond treatment availability. Under the Act on Medical Care for Patients with Intractable Diseases (Intractable Diseases Act),which came into effect in January 2015, a disease is classified as intractable if it meets the following conditions:
- The pathogenic mechanism remains unclear.
- No established treatment options are available.
- The disease is rare.
- Long-term medical care is required.
Notably, this classification is independent of patient numbers. Additionally, diseases with existing specialized measures—such as cancer, mental illness, and infectious diseases—are not included under this category.
Source:
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Definition of Intractable Diseases (January 23, 2015)
What Are Designated Intractable Diseases?
A designated intractable disease is a specific subset of intractable diseases that meet additional criteria under the Intractable Diseases Act:
- The number of patients in Japan remains below a certain threshold (around 0.1% of the population).
- The disease can be diagnosed using objective criteria or equivalent standards.
Upon the implementation of the Act in 2015, 110 diseases were classified as designated intractable diseases. By November 2021, this number had increased to 338. Unlike general intractable diseases, patients with designated intractable diseases qualify for medical expense subsidies, reducing their financial burden.
Source:
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Medical Expense Subsidies for Designated Intractable Diseases (July 27, 2022)
What Are Rare Diseases
A rare disease is defined as a condition affecting fewer than 50,000 patients in Japan—equivalent to less than 0.04% of the population. While the prevalence of each rare disease is low, more than 6,000 rare diseases have been identified worldwide, collectively affecting a significant number of people.
Symptoms of rare diseases vary widely, ranging from immune system deficiencies to localized pain in extremities. Challenges include delayed diagnoses, low public awareness, and limited social support, making timely identification and intervention critical.
Sources:
• Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Designation System for Rare Disease Pharmaceuticals (December 11, 2023)
• Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association, Recommendations on Intractable and Rare Diseases (December 11, 2023)
Differences Between Designated Intractable Diseases and Rare Diseases
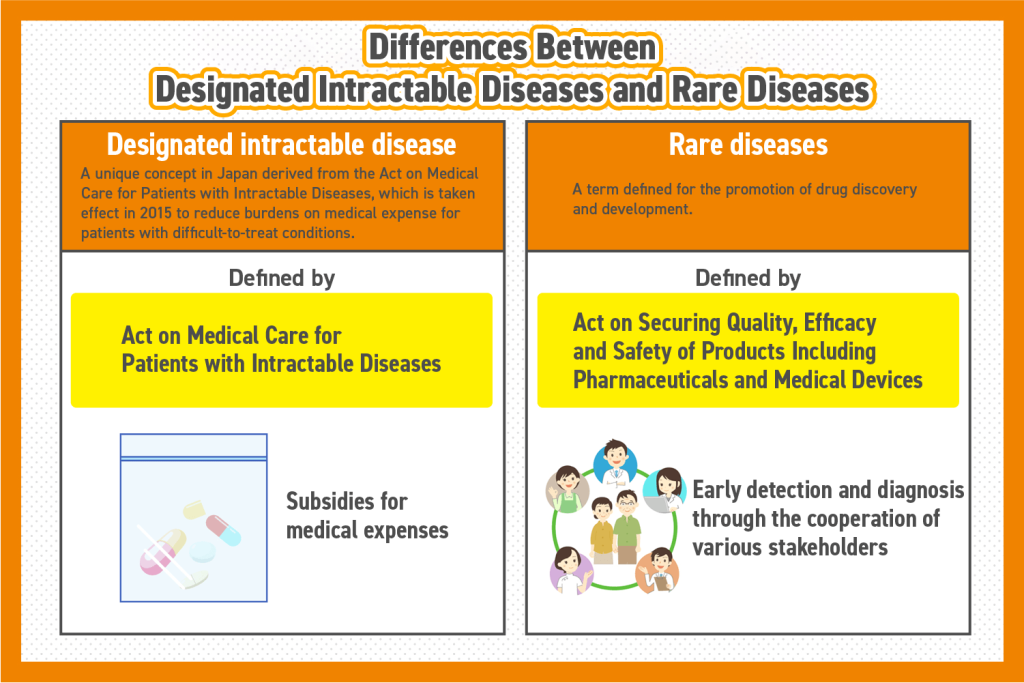
Although both terms describe medical conditions affecting a small population, they are defined under different legislative frameworks:
- Designated intractable diseases fall under the Intractable Diseases Act, primarily aiming to reduce medical costs for patients suffering from conditions without current treatment options.
- Rare diseases are defined under the Act on Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices, focusing on the promotion of drug development.
One key distinction is financial support: while patients with designated intractable diseases receive subsidized medical expenses, individuals with rare diseases do not necessarily qualify for such assistance. However, some rare diseases overlap with designated intractable diseases, granting certain patients access to these benefits.
Approaches to Managing These Diseases
Designated Intractable Disease Initiatives
Since treatment approaches differ by disease and patient condition, physician discretion is vital. Several prefectures in Japan have categorized medical institutions into three roles to improve patient care:
- Core hospitals: Focus on early and accurate diagnosis.
- Specialty core hospitals: Provide specialized treatment and expertise.
- Cooperative hospitals: Offer localized medical care and support.
Source:
Japan Intractable Diseases Research Foundation, Common Questions and Sample Answers (December 11, 2023)
Rare Disease Initiatives
While orphan drug development plays a crucial role in addressing rare diseases, pharmaceutical companies face challenges due to high research costs and uncertain financial returns. To mitigate these barriers, Japan introduced financial support measures in 2013, encouraging drug development for rare conditions.
Additionally, due to the complexity of diagnosing rare diseases, medical associations and academic institutions have developed guidelines to aid general practitioners in early identification.
Source:
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, System for Pharmaceutical Drug Designation and Reexamination Period Extension (2016-10)
Enhancing Awareness and Understanding
Having more than 6,000 rare diseases being discovered in the world, Japan recognizes 338 designated intractable diseases. Each designated intractable disease affects approximately 0.1% of the population, while each rare disease impacts fewer than 0.04%. Given that some conditions remain undiagnosed or undiscovered, increasing awareness and improving diagnostic tools are crucial for better patient outcomes.
A collaborative approach—engaging patients, families, medical professionals, and policymakers—is essential for advancing research, improving healthcare access, and ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those affected by these conditions.