Trends in Osteoporosis Patient Numbers and Use of Newly Listed Guideline Drugs
Osteoporosis is a systemic condition characterized by reduced bone strength, which heightens the risk of fractures and significantly impairs patients’ quality of life (QOL) and activities of daily living (ADL). In particular, proximal femur fractures and vertebral compression fractures are major contributors to the onset of long-term nursing care needs.
In May 2025, the Japan Osteoporosis Society issued its first revision in ten years of the Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. The revision reflects the growing body of evidence supporting newer drugs introduced over the past decade—including romosozumab (Evenity®), zoledronic acid (Reclast®), and abaloparatide (Ostavalo®)—and marks a significant expansion of available therapeutic options.
Using MDV data, we analyzed trends in osteoporosis (M81) patient demographics and usage patterns for osteoporosis treatments (ATC 3rd-level categories and individual generic agents).
1. Monthly Trends in Osteoporosis (M81) Patient Numbers
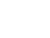
Line chart — Monthly patient numbers for M81, 2019–2024
Data from January 2019 to December 2024 were analyzed, limited to hospitals with complete datasets for all relevant months (360 facilities).
Across the past six years, the number of osteoporosis patients has steadily risen—from approximately 230,000 at the beginning of 2019 to around 250,000–260,000 by late 2024.
2. Year-on-Year Comparison of Monthly Osteoporosis (M81) Patient Numbers
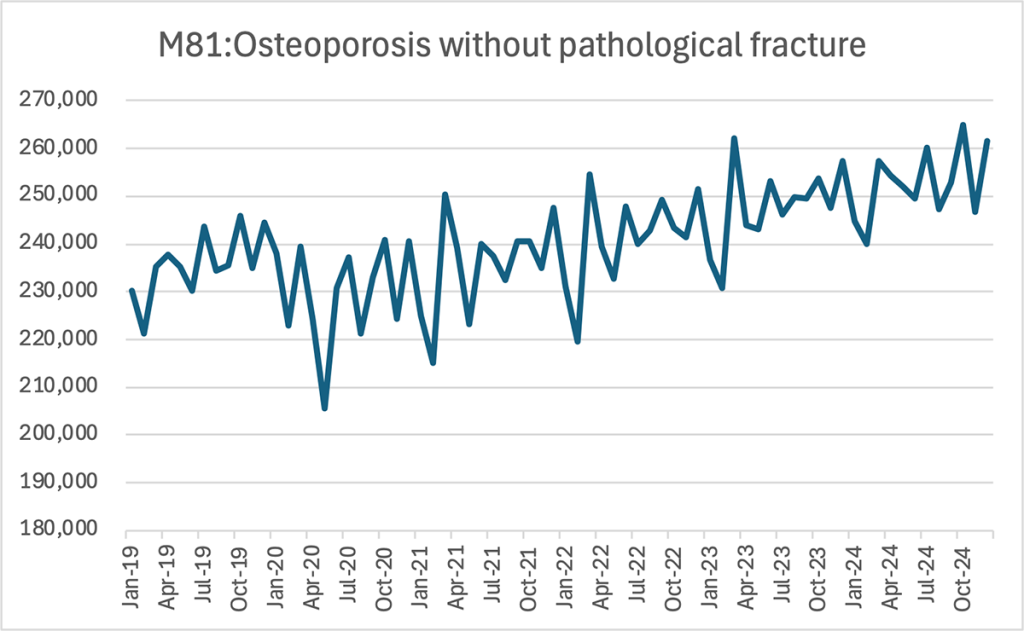
Multi-line chart — Monthly patient counts by year
The analysis shows that patient counts have been trending upward each year, with 2023 and 2024 consistently exceeding prior years. Monthly patterns indicate noticeable peaks in March and October, while February and May tend to show dips.
3. Annual Trends in Patients Prescribed Osteoporosis Treatments (ATC 3rd Level)

Stacked bars — Annual patient counts by ATC 3rd-level drug class
Total annual patient numbers receiving osteoporosis medications increased from roughly 222,000 in 2019 to about 251,000 in 2024.
Bisphosphonates—classified as “Drugs for Osteoporosis and Related Disorders” (green bars)—remain the most widely used group, though the increase has been modest (from about 165,000 patients in 2019 to 173,000 in 2024).
Meanwhile, “Other Agents Affecting Bone and Calcium Metabolism” (blue) show a marked rise—from approximately 42,000 patients in 2019 to 64,000 in 2024. This growth appears to be driven primarily by expanded use of high-potency agents such as denosumab and romosozumab, both among newly diagnosed patients and those switching from previous therapies.
4. Annual Trends in Expenditures for Osteoporosis Treatments (ATC 3rd Level)
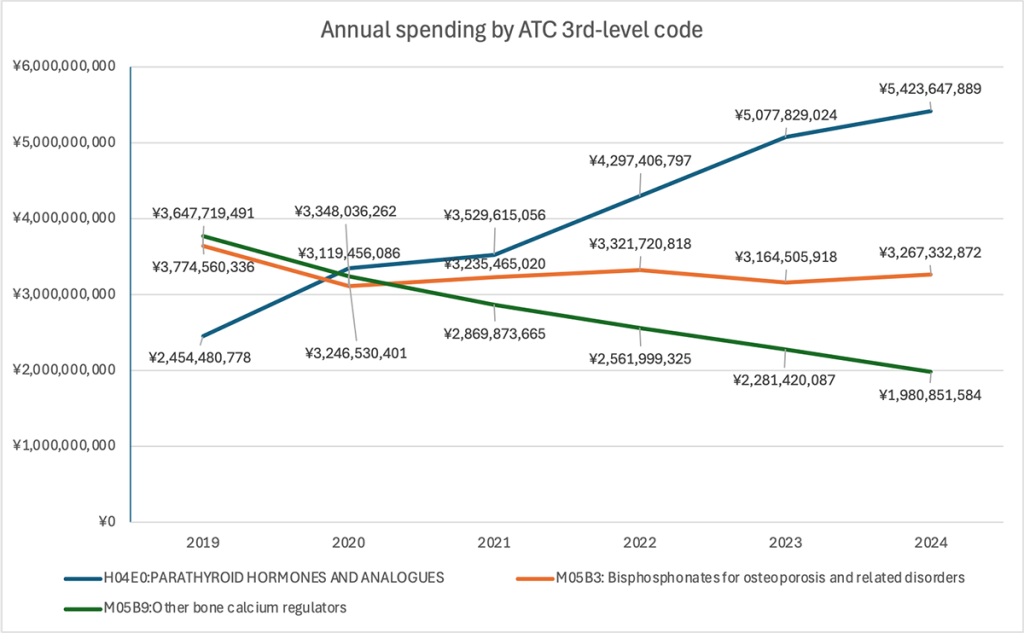
Line + stacked bars — Total annual drug spending by class
Overall spending increased from roughly ¥9.87 billion in 2019 to ¥10.68 billion in 2024, but the composition changed significantly.
Spending on “Other Agents Affecting Bone and Calcium Metabolism” (blue line) more than doubled—from about ¥2.45 billion in 2019 to ¥5.42 billion in 2024—and has been the largest expenditure category since 2021.
In contrast, spending on bisphosphonates fell sharply—from around ¥3.64 billion in 2019 to ¥1.98 billion in 2024—despite the rise in the number of patients receiving these drugs. The decline likely reflects broader use of generics and lower unit prices. At the same time, the steep spending increase in “Other Agents” aligns with both higher prescription volumes and the inherently higher prices of agents like denosumab and romosozumab.
5. Trends Among the Top Five Osteoporosis Drugs by Number of Prescribed Patients
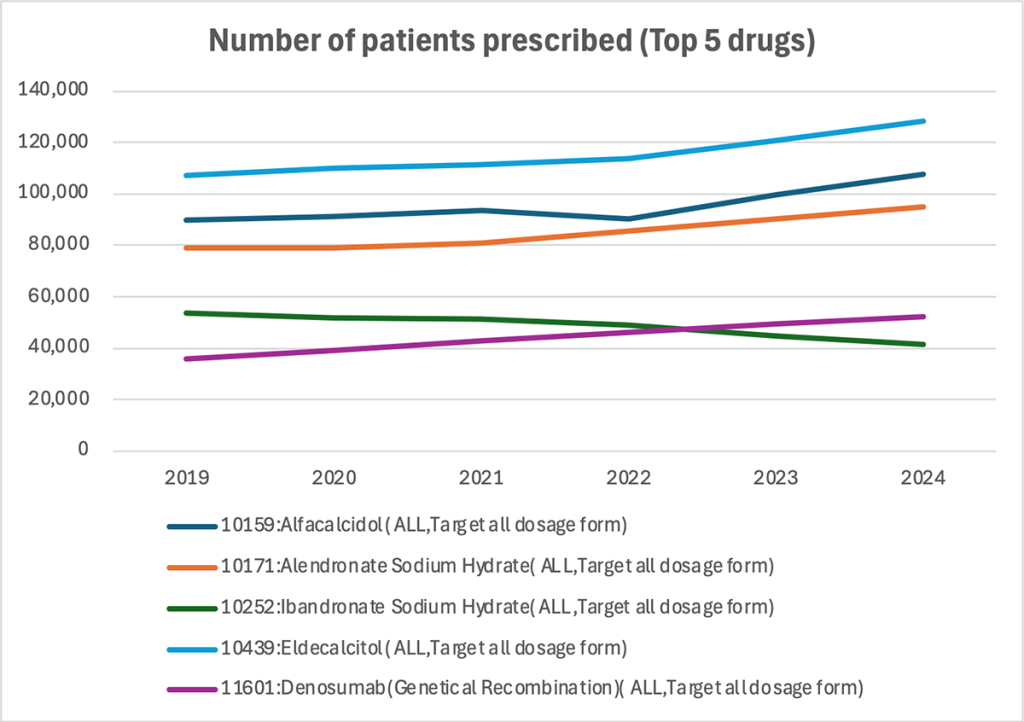
Multi-line chart — Annual patient numbers for top 5 drugs
Among all osteoporosis treatments, the top five drugs were analyzed by patient count.
Eldecalcitol (blue line), the most used active vitamin D3 formulation, remains the drug with the highest patient numbers—rising to about 130,000 in 2024.
Among bisphosphonates, alendronate sodium hydrate (orange) has the largest user base, maintaining a stable range of roughly 80,000–90,000 patients.
Denosumab (purple), an anti-RANKL monoclonal antibody, has grown steadily since 2019 and reached approximately 50,000 patients in 2024. This rise mirrors the increasing prominence of “Other Agents Affecting Bone and Calcium Metabolism” observed in the ATC-category analysis and suggests a strengthening market presence.
6. Trends Among the Top Five Osteoporosis Drugs by Expenditures
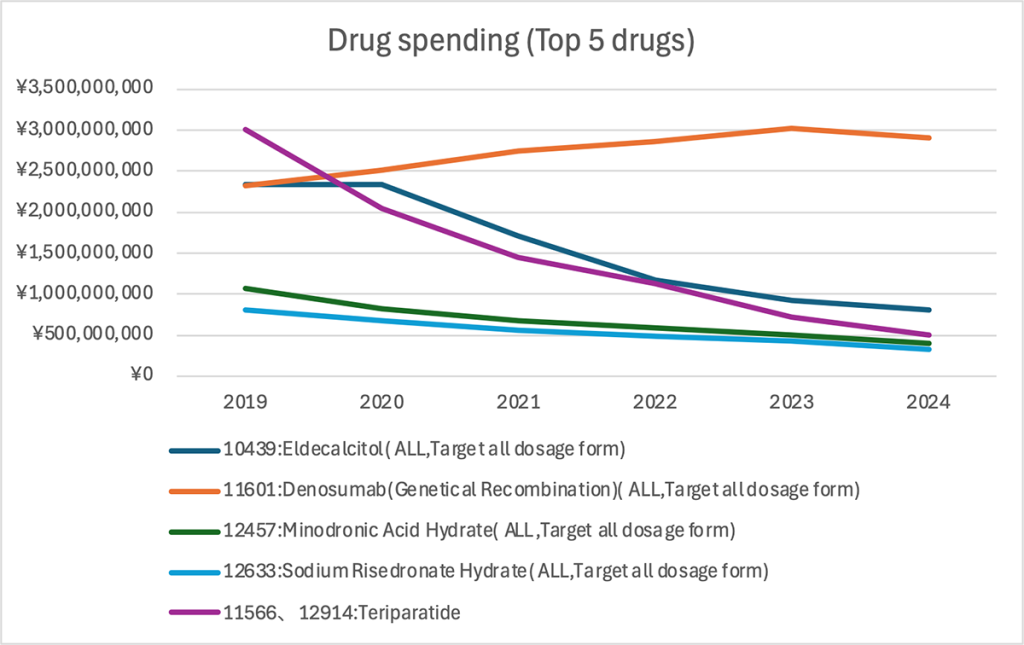
Multi-line chart — Annual expenditure for top 5 drugs
Finally, the top five drugs were analyzed by total spending.
Denosumab (orange line) has been the highest-spend drug since 2020, surpassing ¥3 billion in 2023 before dipping slightly to around ¥2.9 billion in 2024.
Teriparatide (purple), a parathyroid hormone (PTH) analog, led the market in 2019 at almost ¥3 billion, but expenditures have plummeted since then—falling below ¥500 million in 2024. The rapid decline likely reflects the introduction of biosimilars and a shift toward alternative bone-forming agents.
Eldecalcitol (navy) was stable at around ¥2.3 billion through 2020 before declining to roughly ¥800 million by 2024. Meanwhile, the bisphosphonates minodronic acid hydrate (green) and risedronate sodium hydrate (light blue) continued downward trends, each reaching about ¥300 million in 2024.
Overall, denosumab’s dominance in expenditures reflects the combination of high unit cost and a growing treated population. Conversely, teriparatide’s steep decline demonstrates the impact of biosimilar uptake and evolving therapeutic strategies.
Note: This article was published on December 1, 2025.
Data survey and analysis tailored to your specific requests
Databases, data analysis requests, and more.
© Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.