Trends in the Number of Hospitalized Patients in the Designated Intractable Disease Area -Analysis of DPC Data-
Rare and intractable diseases are characterized by a limited number of patients, while often requiring long-term treatment. In the consideration of research and development strategies as well as healthcare delivery systems, it is therefore essential to accurately understand the actual patient population based on real-world clinical data. The last day of February each year is designated as Rare Disease Day (RDD), an international awareness day aimed at promoting understanding of rare and intractable diseases.
In Japan, designated intractable diseases are defined as diseases designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare based on criteria including unknown etiology, lack of established treatment methods, rarity, and the need for long-term medical care. As of April 2025, a total of 348 diseases have been designated.
Based on the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare’s List of Designated Intractable Disease Names and Clinical Survey Individual Forms, designated intractable diseases were identified, and trends in the number of hospitalized patients by fiscal year were analyzed using MDV’s DPC data from April 2023 onward.
Specifically, this report summarizes:
- the top 10 designated intractable diseases by number of hospitalized patients (Table 1);
- the top 10 diseases with the highest number of hospitalized patients in the neurological and neuromuscular disease area (Table 2);
- the top 10 diseases in the immune system disease area (Table 3); and
- trends in the number of hospitalized patients for diseases targeted by orphan drugs approved in fiscal years 2023–2024 (Table 4).
For inquiries regarding the use of the MDV database for analyses of designated intractable diseases and rare diseases, please feel free to contact us.
1. Ranking of Hospitalized Patients with Designated Intractable Diseases Based on DPC Data
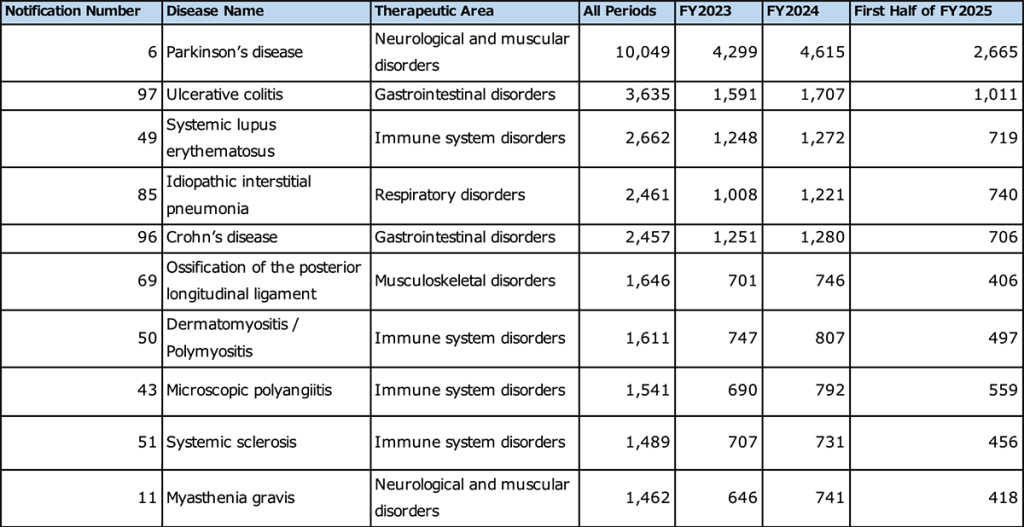
Study period: April 2023 – September 2025
Number of facilities: 445
Among the 445 facilities included in the analysis, Parkinson’s disease had by far the largest number of unique hospitalized patients (10,049 patients), followed by ulcerative colitis (3,635 patients) and systemic lupus erythematosus (2,662 patients). From fiscal year 2023 to fiscal year 2024, all of the top 10 diseases showed an increasing trend in the number of patients. In addition, four of the top 10 diseases belong to the immune system disease category, highlighting a notable increase in hospitalized patients in this area.
In terms of year-on-year trends, several diseases — including ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and microscopic polyangiitis — showed increases of approximately 6% to 14% in the number of hospitalized patients between fiscal years 2023 and 2024. These findings indicate a steady expansion in the acceptance of patients with intractable diseases at DPC hospitals.
2. Ranking of Hospitalized Patients in the Neurological and Neuromuscular Disease Area

Study period: April 2023 – September 2025
Number of facilities: 445
Focusing on year-by-year trends in the neurological and neuromuscular disease area, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy / multifocal motor neuropathy showed an increase of approximately 17% (from 205 to 240 patients), while corticobasal degeneration increased by approximately 18% (from 136 to 161 patients). In the first half of fiscal year 2025, patient numbers already exceeded half of the previous year’s total, suggesting a continued inflow of patients to DPC hospitals or increased disease identification due to improved diagnostic accuracy.
While some diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and spinocerebellar degeneration, involve patient populations on the order of 1,000 individuals, the relatively high growth rates observed in ultra-rare diseases suggest increasing centralization of care at specialized medical institutions.
3. Ranking of Hospitalized Patients in the Immune System Disease Area

Study period: April 2023 – September 2025
Number of facilities: 445
In the immune system disease area, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis / polymyositis, and microscopic polyangiitis accounted for the largest numbers of hospitalized patients. Comparing fiscal years 2023 and 2024, increases of approximately 10% to 30% year on year were observed for diseases such as microscopic polyangiitis (from 690 to 792 patients) and eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (from 264 to 348 patients).
Advances in diagnostic technologies and the wider adoption of new therapeutic agents may have contributed to the observed increase in patient numbers within the DPC data.
4. Trends in the Number of Hospitalized Patients for Diseases Targeted by Drugs Approved in Fiscal Years 2023–2024

Study period: April 2023 – September 2025
Number of facilities: 445
Among diseases targeted by orphan drugs approved over the past two fiscal years, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (1,138 patients), immune thrombocytopenia (1,250 patients), and myasthenia gravis (1,462 patients) stand out as having relatively large numbers of hospitalized patients even within the rare disease category. In contrast, diseases such as distal myopathy (7 patients) and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (20 patients) had extremely small numbers of hospitalized patients.
In addition, pulmonary arterial hypertension, for which a drug was approved in fiscal year 2024, showed a sharp increase of approximately 39% year on year (from 163 to 227 patients). This increase is considered to reflect an acceleration in patient visits to specialized medical institutions following the introduction of a new therapy, providing evidence that drug approvals can influence patient healthcare-seeking behavior.
References
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA): List of Newly Approved Drugs (Fiscal Years 2023 and 2024)
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: List of Designated Intractable Disease Names and Clinical Survey Individual Forms
Note: This article was published on February 2, 2026.
Data survey and analysis tailored to your specific requests
Databases, data analysis requests, and more.
© Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.