News
After the COVID-19 transitioned to category 5 infection, the number of patients has been slowly recovering. Aspiration pneumonia increased in respiratory diseases, possibly due to behavioral restrictions and extreme heat
- November 10, 2023
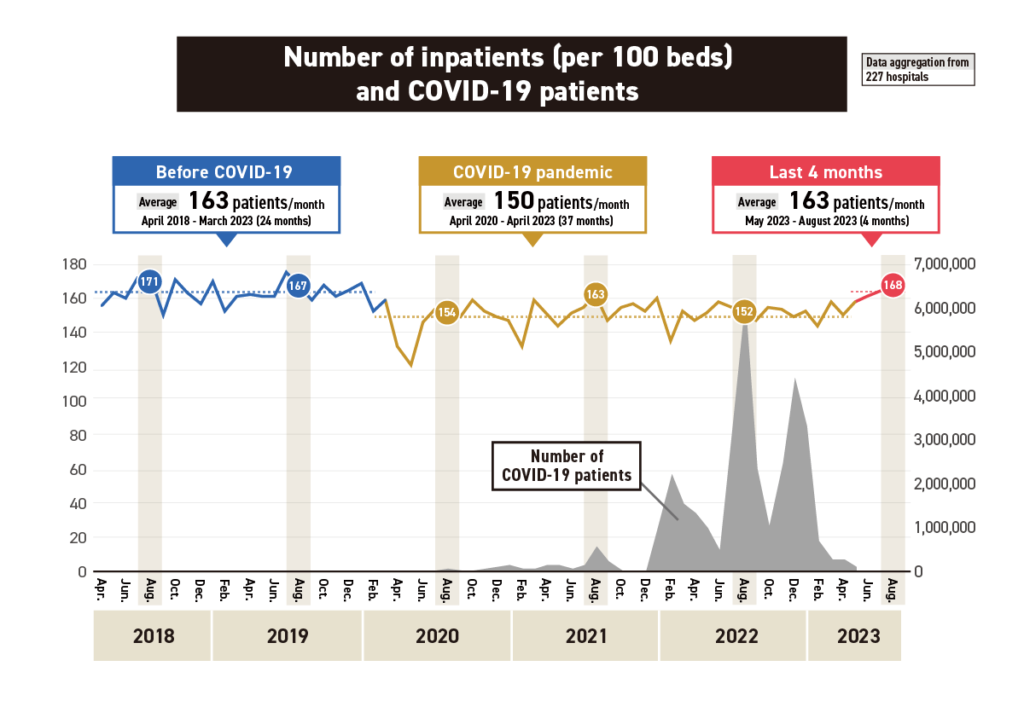
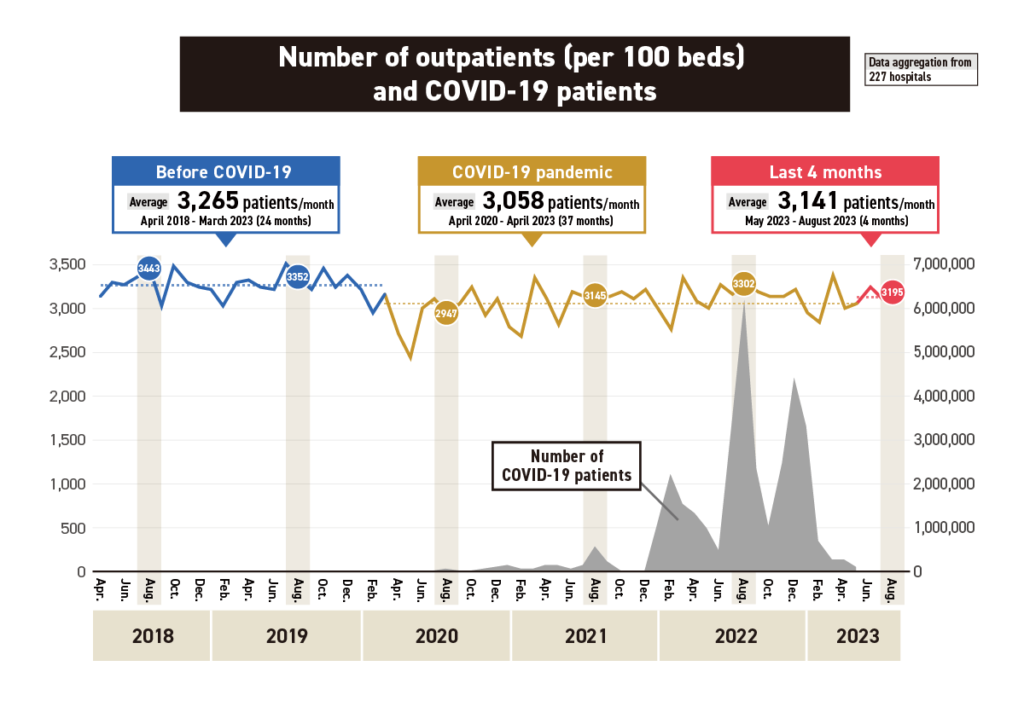
Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. (Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President: Hiroyuki Iwasaki), which has one of the largest medical databases (DB) in Japan, has analyzed patient visit behavior before and after the outbreak of the new coronavirus. The number of patients, which declined sharply after the coronavirus disaster due to patients’ reluctance to receive medical care, showed a recovery trend after being moved to Category 5 under the Infectious Disease Control Law on May 8 of this year.
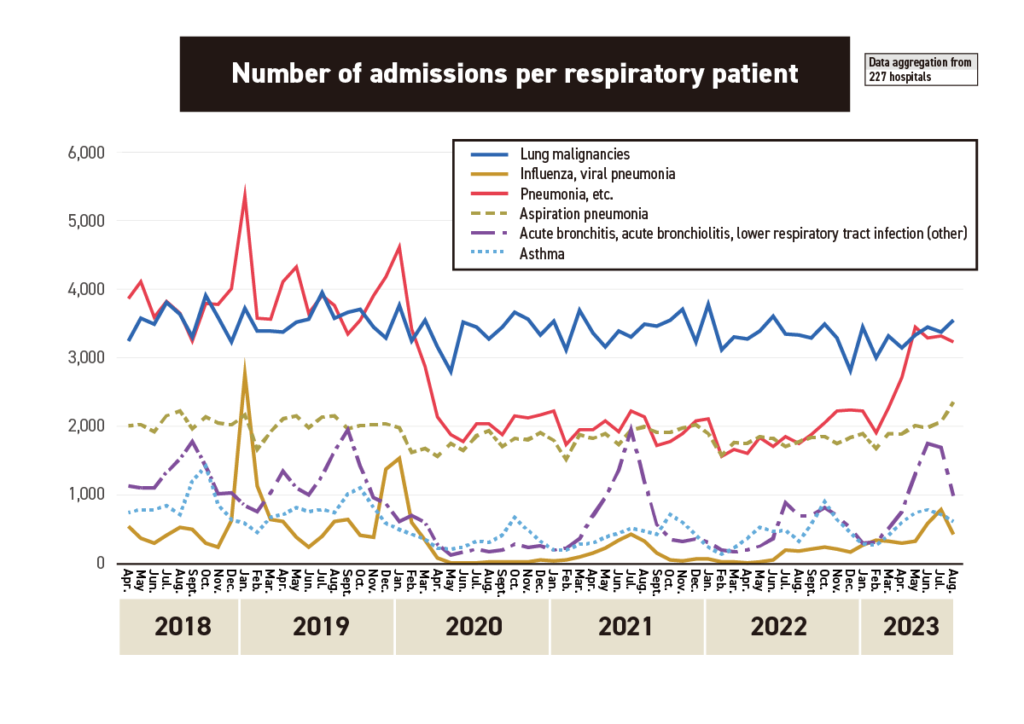
Furthermore, when we took a closer look at respiratory diseases, it became apparent that aspiration pneumonia is on the rise. It is speculated that this increase may be attributed to factors such as the restrictions imposed during the COVID-19 pandemic and extreme heat.
This database analysis was conducted under the following conditions:
Analysis periodApril 2018 – August 2023Number of facilities227 facilities for which data were available for the above aggregation periodMDV’s medical databasesHospital data:
Number of patients 45.25 million
493 facilities
(as of October 31, 2023)
Insurer data:
Number of patients 19.70 million
661 organizations
(same as above)
Jiseikai Social Medical Corporation (Adachi-ku, Tokyo)
Masashi Ito, Chairman of the Board and Director, Tojun Hospital
During the COVID-19 outbreak, there were concerns about the new coronavirus infection, leading to a tendency among patients to avoid seeking medical care. Additionally, in some cases, non-urgent surgeries were postponed based on the doctor’s judgment. However, for lung cancer surgeries among inpatients with respiratory system diseases, many cases were deemed “necessary” and “urgent.” As a result, the number of such surgeries did not experience a significant decline before, during, or after the COVID-19 outbreak.
On the other hand, the recent sharp increase in cases of aspiration pneumonia may be attributed to the current situation in which a significant number of elderly patients are being transported to our hospital as emergency cases. It can be speculated that not only elderly individuals who have been in a prolonged bedridden state for over three years during the COVID-19 pandemic but also those who were elderly with a high level of self-sufficiency have experienced an advancement in frailty.
Furthermore, the long-lasting impact of the scorching heat has also contributed to a decrease in activities of daily living (ADL), leading to aspiration pneumonia triggered by some event and resulting in hospitalization in several cases.
We can also learn about influenza from the past, which saw a spike from September 2019 to the end of the year. At that time, the Rugby World Cup was being held in Japan (October 19-November 2 of the same year), and one factor was that many people from the southern hemisphere, where many countries participate, came to Japan during the flu epidemic around that time, leading to a sharp increase in influenza cases.
However, the coronas were moved to Category 5 under the Infectious Disease Control Law on May 8, and as caution against coronas is further lowered toward the end of the year and infection control measures become more sparse, the flow of people back into town, plus factors such as an increase in travelers from overseas due to the weak yen, may lead to a sharp rise in influenza cases. The number of influenza patients may increase sharply. It will be important to protect oneself by wearing a mask in places where people gather, a habit that should have been acquired through the coronary disaster.