News
A working graduate student’s research using medical big data wins the Japan Diabetes Society Award for identifying clues to reducing hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- June 20, 2025
A medical big data study conducted by Miho Kageyama, a working graduate student, and others under the supervision of Lecturer Takeshi Horii at the Clinical Pharmacy Center, School of Pharmacy, Musashino University (Nishitokyo City, Tokyo; University president: Seiko Nishino), revealed a gradual decline in hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia among patients with type 2 diabetes. This research was awarded the 9th Excellent Presentation Award for Medical Staff by the Japan Diabetes Society.
The study utilized medical data from the nation’s largest clinical database provided by Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. (Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President and CEO: Hiroyuki Iwasaki; hereinafter “MDV”), which contains data from approximately 52.37 million real patients as of the end of May 2025. Ms. Miho Kageyama, a licensed pharmacist, serves as a lecturer at the Practical Training Education Center, School of Pharmacy, Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, while also continuing her research as a working graduate student at the Clinical Pharmacy Center, School of Pharmacy, Musashino University. This study analyzed clinical data from January 1, 2009, to December 31, 2022, focusing on patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and hypoglycemia, to assess the risk of severe hypoglycemic events requiring hospitalization.
Regarding the study’s receipt of the Japan Diabetes Society’s Excellent Presentation Award for Medical Staff, Mr. Horii, the academic advisor to Ms. Kageyama, commented:
“This research was made possible thanks to the detailed information available at the time of hospitalization within MDV’s DPC data. I believe it was recognized for offering a unique perspective distinct from studies using other databases. Through this study, I truly came to appreciate the extensibility and comprehensiveness of MDV data, which enable the resolution of a wide range of clinical questions.”
Comment from Ms. Kageyama:
“As a pharmacist, I explain the importance of preventing and managing hypoglycemia to patients at the pharmacy counter. However, the outcomes of such preventive efforts are often difficult to see. Through this study, we were able to visualize initiatives by the Japan Diabetes Society using big medical data analysis. It also reaffirmed for me how crucial the proper use of medications is to ensuring their safe application.”

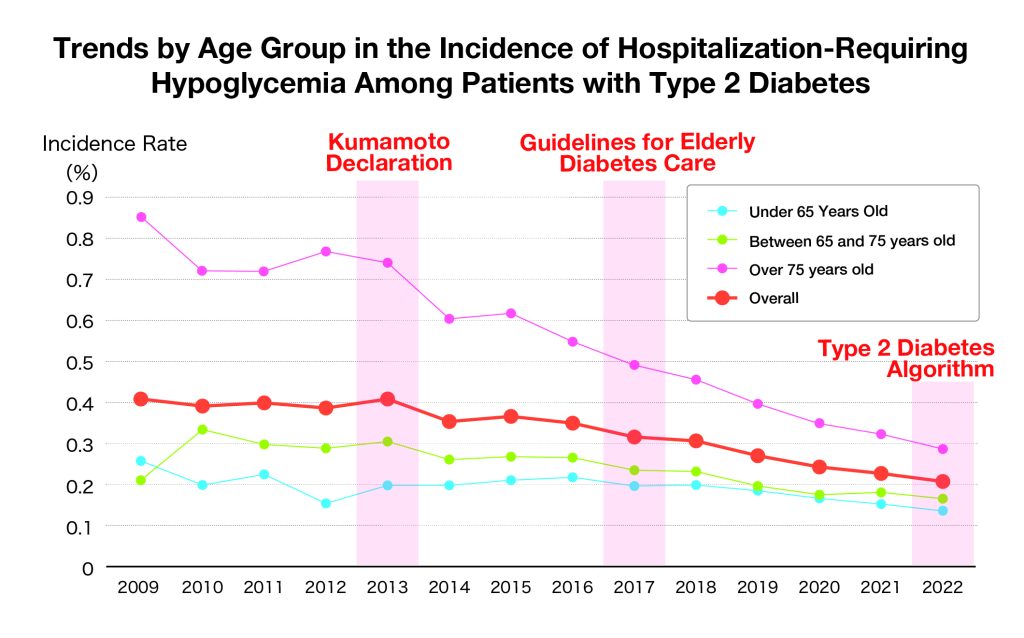
The study results showed that key turning points such as the so-called “Kumamoto Declaration” in 2013, in which the Japan Diabetes Society set a target HbA1c (hemoglobin A1c) level of less than 7% for glycemic control, and the revision of the Society’s Guidelines for Elderly Diabetes Care in 2017 served as game changers, leading to a significant decline in the incidence of hypoglycemia, as illustrated in the graph below. The introduction of new antidiabetic medications is also believed to have contributed to this trend. Additionally, nearly 60% of hospitalized patients with hypoglycemia were aged 75 or older.
Previous studies have shown that individuals with a BMI (Body Mass Index), an international indicator of obesity, below 18.5 (classified as underweight) tend to have a higher proportion of hospitalizations due to hypoglycemia. In this study as well, the proportion of such patients was calculated and found to be 16.7%, confirming a similarly high trend consistent with previous findings.