What is Drug Discovery? Explaining the Drug Development Process in Japan and AI-Driven Drug Discovery
Drug discovery identifies compounds effective against diseases and develops them into approved medicines. Recent advancements in AI are improving efficiency across the drug-development process. This article explains the process in Japan and highlights key aspects of conducting drug discovery.
What is Drug Development ?
In simple terms, drug development is the process of creating new medicines. Before a medicine can be used in hospitals or clinics, it must go through several stages: discovering the active compound, conducting basic research and clinical trials, and obtaining approval from the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). The drug discovery process typically takes 10 to 18 years and can cost around 20 billion yen, requiring substantial time and investment.
Differences Between Drug Development and Drug Discovery
The process of creating a new medicine is usually divided into two major phases: drug discovery and drug development. Drug discovery represents the initial phase, in which researchers evaluate thousands of compounds to identify a small number of promising candidates with potential therapeutic effects. These compounds are then refined and tested to determine whether they can be developed into safe and effective medicines.
Drug development refers to the subsequent process of transforming these candidates into approved products. It includes preclinical and clinical studies, regulatory submissions, and post market surveillance (PMS), while also focusing on the continuous optimization of medicines after they are prescribed to further improve their safety and efficacy.
The Drug Development Process
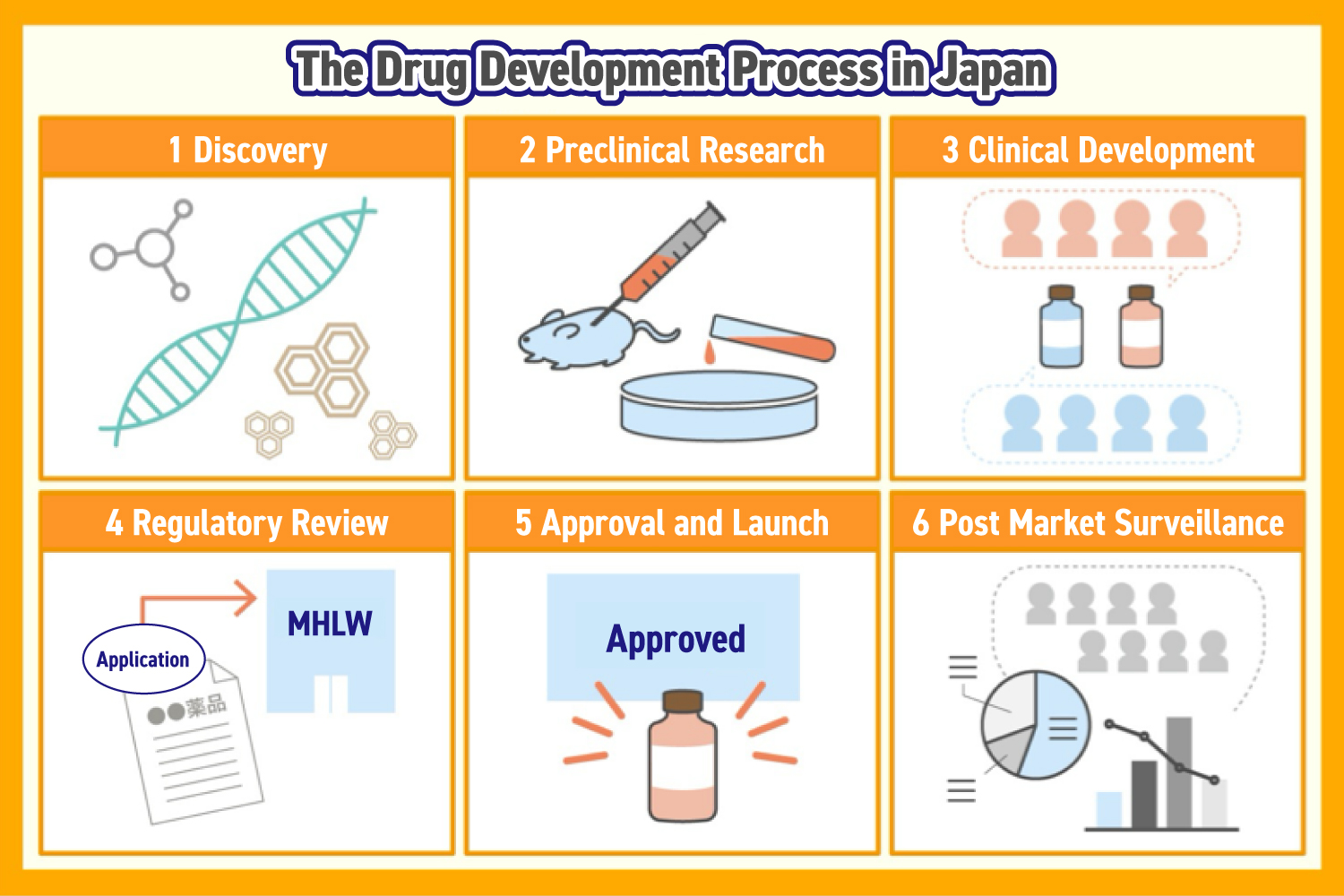
Drug development usually follows five key stages, beginning with drug discovery and continuing through regulatory approval and market launch. Once a drug reaches patients, development continues with further studies to refine its use and improve safety and efficacy.
Drug Discovery
Researchers evaluate thousands of candidate compounds. These may originate from natural sources such as plants or microorganisms, as well as from synthetic chemistry, biotechnology, or genomic research.
Preclinical Research
At this stage, experiments are conducted on animals or cultured cells, to evaluate the efficacy and safety of candidate compounds, including absorption, metabolism, excretion, and overall safety.
Clinical Development
Today, SoV has evolved. Companies now track brand presence across scientific publications, digital channels, and professional discussions, shifting the focus from quantity to quality. Modern SoV concepts like Scientific Share of Voice, Share of Insight, and Share of Care emphasize meaningful clinical information, support for physician decision-making, and collaborative solutions with patients and HCPs.
The Positioning Strategy
Clinical trials test the investigational drug on humans whose safety was confirmed in non-clinical trials. They are divided into three phases:
- Phase 1
A small group of healthy volunteers takes part to confirm the drug’s safety and detect any potential side effects. - Phase 2
A small group of patients tests the drug to assess its efficacy, determine a safe dosage, and identify the best administration methods. - Phase 3
A larger group of patients participates to compare the drug’s safety and effectiveness with existing treatments.
Regulatory Approval
Once clinical trials confirm safety, efficacy, and quality, an application is submitted to the MHLW. The Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and the Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC) review the application according to Japanese regulations.
Approval and Market Launch
Following regulatory approval in Japan, manufacturing and market launch can start. For new drugs covered by Japan’s National Health Insurance, the MHLW sets pricing based on the standardized drug price system.
Post Market Surveillance
Once a drug is on the market, its use across diverse patient populations is closely monitored to update treatment guidelines and identify potential side effects. Continuous evaluations of safety and efficacy are required by law.
What is AI Drug Discovery?
AI-driven drug discovery improves the efficiency of developing new medicines and therapies by analyzing large datasets and generating actionable, data-driven insights. This technology also supports target identification and lead compound selection, reduces reliance on human intuition, and helps shorten development timelines while lowering costs.
Why AI Drug Discovery is in the Spotlight and the Future of the Pharmaceutical Industry
Current challenges in drug discovery include:
- Low success rates (approximately 1 in 13,000 compounds)
- Inefficiencies throughout the drug development process
The probability of success has dropped significantly over the past 20 years, making data-driven approaches increasingly important for efficient drug development.
Resolving Issues in Drug Discovery with AI
By analyzing large datasets quickly and accurately, AI enables pharmaceutical companies to prioritize high-potential compounds, streamline experimental processes, and optimize development timelines. As more companies adopt AI in their R&D pipelines, the industry is moving toward more efficient, cost-effective, and predictable medicine development.
How AI and Big Data Can Make Drug Discovery More Efficient
AI and big data enable smarter, faster drug development by transforming vast amounts of data into actionable insights. At MDV, we provide products and services tailored for pharmaceutical companies to support AI-driven drug discovery, including market analysis for new development opportunities. Companies seeking to optimize their drug development processes are encouraged to contact us for consultation.
For More Information, Please Contact Us Here
About Japanese Healthcare System

What you need to know about the healthcare system in Japan before using the data.
SERVICE

In addition to various web tools that allow you to easily conduct surveys via a browser using our medical database, we offer data provision services categorized into four types to meet your needs and challenges: "Analysis reports" "Datasets," "All Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service," and "Specific Therapeutic Areas Data Provision Service.

© Medical Data Vision Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.